Custom Plastic Profile Extrusion
Since our start in 1993, BD Custom Manufacturing has been dedicated to creating high-quality plastic profile extrusion products designed to meet any set of specifications. We offer an extensive customization process that allows us to provide custom-molded PVC and polyethylene products for a growing number of manufacturing sectors across the country, including:
• RV industry
• Construction industry
• Upholstery and furniture industry
• Marine industry
• Automotive industry
• Point of purchase display
• Sign companies
• Exhibit manufacturers
• Building products
• Agriculture
• Consumer goods
Plastic Profile Extrusion Manufacturing Process
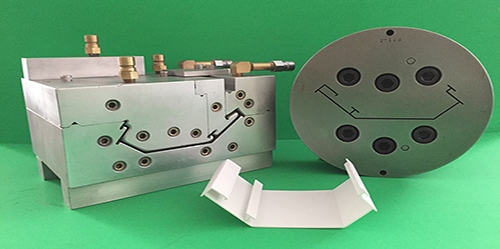
Plastic extrusion is an intricate process that involves melting plastic and reconstituting it into a specified configuration. Plastic materials are poured into a hopper, which then feeds the material into a heated barrel.
Next, the melted plastic passes through a screen and into a die that shapes it according to the desired specifications. Plastic extrusion is a popular choice for many different manufacturing applications because it allows for large production volumes at relatively high speeds with low production costs. Some common plastic products made by extrusion include piping and tubing, window frames, weather stripping, and wire insulation.
Customers from all industries have come to rely on BD Custom Manufacturing for our impressive custom-designed tooling, ability to perform small runs, and fast turnaround times. We specialize in the production of custom polyethylene and PVC profiles and offer a diverse selection of configurations, colors, thicknesses, and lengths.
This versatility allows us to manufacture products to meet your exact specifications, no matter how complex. We have the manufacturing capabilities to handle projects of any size, large or small.
Your Top Choice for Custom Plastic Profile Extrusion
Our experienced personnel, high standards of quality control, and constant process improvement enable us to consistently meet or exceed the plastic profile extrusion needs of our customers. As extrusion technologies are constantly evolving, you can count on us to offer the most cutting-edge plastic extrusion methods and materials. As one of our valued customers, you can expect:
• Quick lead times: We are committed to providing quick lead times to ensure our customers receive their orders as fast as possible. Once we receive an order accompanied with a die, you can expect a lead time of approximately 10 working days.
• High-level quality control: Quality control practices are embedded in all aspects of our manufacturing operations. We are constantly improving our processes to ensure that each manufactured part meets the highest level of accuracy and precision. Our goal is to protect you from the inconveniences and delays associated with manufacturing dilemmas and faulty parts.
• Expert tooling design capabilities: If you are starting a new project or would like to replace your current tooling, we have the resources and expertise necessary to design a high-quality extrusion die according to your exact specifications.
• Access to vacuum calibration tooling: We offer vacuum sizing dies and tooling to produce plastic parts with complicated or dimension-critical design features. The vacuum sizing process applies vacuum pressure to the external surface of the plastic profile during the calibration process, allowing for the formation of a consistent plastic part that meets predetermined specifications. This procedure is often used to ensure roundness, such as with the extrusion of tubing, and for producing parts that require a true 90-degree angle.
Contact BD Custom Manufacturing Today
One of our core strengths as a plastic profile extrusion company is our dedication to going above and beyond to satisfy our customers. We take pride in our ability to think outside of the box to provide innovative solutions for the most complex customer challenges.
To learn more about how we can help you with your custom plastic extrusion needs, call us at (574) 848-0925, contact us online, or request a quote today.